The order in which Registry entries are assigned
In general, Registry permissions can be set for:
- A user
- A group
- System-wide
When a user logs in to EMu a search is performed in the Registry to determine what permissions have been set for the user. The System looks for Registry entries in this order:
- Entries for the user.
- Entries for a group to which the user belongs.
- Entries that apply system-wide.
When a match is found, the search ends. In other words, a permission set for a user has precedence over a permission set for a group, which has precedence over a system-wide setting.
IMPORTANT: For each Registry entry, it is not possible simply to document the differences between an individual user's permissions and those of a group to which the user belongs. User and group permissions for the same Registry entry are not cumulative: a user Registry entry overrides the equivalent group Registry entry.
User Fred is a member of group Managers. Let's say we want group Managers to view records and we want user Fred to edit them as well. We cannot have one entry that provides group Managers with the View permission and one for user Fred with the Edit permission. When a user logs in to EMu, the System first looks for entries for the user and stops searching if a match is found, so in this case user Fred would only have the Edit permission. It is necessary to have an entry that provides group Managers with the View permission and one for user Fred with the View and Edit permissions.
The EMu Administrator is typically concerned with two types of Registry entries:
Customizations and configurations that should be effective across the system are set with a System|Setting Registry entry. The structure of this type of entry is:
System
|
Setting
|
subkey1
|
subkey2
|
...
|
value |
It is possible to customize the system so that different users and groups have different values for the same setting.
Each time the System looks up a System|Setting Registry entry, it looks for entries in the following order:
| 1. | User
|
user | Setting
|
subkey1
|
subkey2
|
...
|
value |
| 2. | Group
|
group | Setting
|
subkey1
|
subkey2
|
...
|
value |
| 3. | System
|
Setting
|
subkey1
|
subkey2
|
...
|
value |
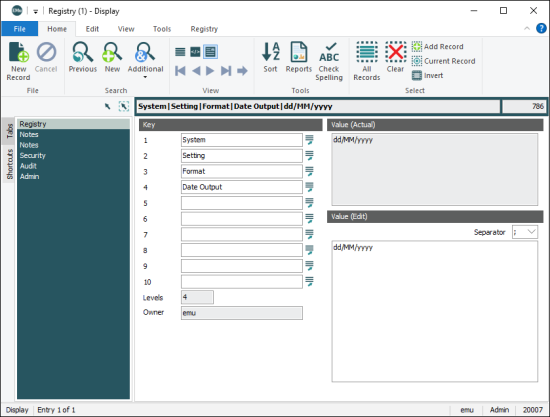
The following is an example of how EMu checks for a System setting for a user. Consider an entry that tells the System in what format dates should be displayed:
A user has the username emu and is in group Admin. The Registry is searched for an entry that defines the date format to be displayed when emu logs in to EMu:
|
Order |
Description |
Search Details |
Results |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
The Registry is searched for an entry for Date Output that is defined for user |
|
If this entry exists, the value associated with it will be used as the Date Output format for user |
|
2 |
If the above entry does not exist, the System searches for an entry for group |
|
If this entry exists, the value associated with it will be used as the Date Output format for all members of group Admin, which includes user |
|
3 |
If the above entry does not exist, the System searches for a group |
|
If this entry exists, the value associated with it will be used as the Date Output format for every group, which includes user |
|
4 |
If the above entry does not exist, the System searches for an entry that applies to all users. |
|
This entry will exist, and its value will be used as the Date Output format for everyone, including user |
While configurations can be applied to individual users and groups, others can be applied to individual tables and even columns for each user or group. In this way the System can be customized such that EMu's behaviour can be quite different from user to user.
As with System Setting entries, when looking for Table and Column entries the System first looks for a user entry; if a user entry is not located, a more generic entry is sought that can be applied to the user.
Generally the queries are in the following form and precedence:
User
|
user | Table
|
table | Setting | column | value |
User
|
user | Table
|
table | Setting | Default
|
value |
User
|
user | Table
|
Default
|
Setting | column | value |
User
|
user | Table
|
Default
|
Setting | Default
|
value |
Group
|
group | Table
|
table | Setting | column | value |
Group
|
group | Table
|
table | Setting | Default
|
value |
Group
|
group | Table
|
Default
|
Setting | column | value |
Group
|
group | Table
|
Default
|
Setting | Default
|
value |
Group
|
Default
|
Table
|
table | Setting | column | value |
Group
|
Default
|
Table
|
table | Setting | Default
|
value |
Group
|
Default
|
Table
|
Default
|
Setting | column | value |
Group
|
Default
|
Table
|
Default
|
Setting | Default
|
value |
The queries begin by looking for an entry that is specific to a user, table and column within that table. In the absence of such an entry, the search continues for an entry that is applied System-wide regardless of user, table, or column.
As soon as an entry is found, the value for that entry is applied to the user and no more querying takes place.
A setting of Default may be used where a group, user, table or column is expected. This specifies that the entry can apply to all groups, all users, all tables, or all columns.
In the entries above, Setting is the name of the entry, and may span several keys to achieve the desired precision. Consider the following entry:
Group
|
Registrations
|
Table
|
ecatalogue
|
Security
|
Display
|
SecRecordStatus=Active
|
In this entry the Setting contains two keys, Security and Display. Consult the Registry documentation to find out the precise syntax for a particular entry.
Example
The following is an example of how the System will check for a Table setting for a user. The user has the username emu and is in group Admin. The System is looking for an entry that defines the type of access user emu has to the eparties table:
|
Order |
Description |
Search Details |
Results |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
The System looks for an Operations entry that is defined for user |
|
If this entry exists, the value associated with it defines the table operations for user |
|
2 |
If the above entry does not exist, the System searches for an entry for user |
|
If this entry exists, the value associated with it defines the table operations for user |
|
3 |
If the above entry does not exist, the System searches for an entry for group |
|
If this entry exists, the value associated with it defines the table operations for the Parties module when accessed by group Admin, which includes user |
|
4 |
If the above entry does not exist, the System searches for an entry for group |
|
If this entry exists, the value associated with it defines the table operations for all tables accessed by group Admin, which includes user |
|
5 |
If the above entry does not exist, the System searches for an entry for all groups and all tables. |
|
If this entry exists, the value associated with it defines the table operations for all tables accessed by all groups, which includes user |